**Cumin Production and Trade**
– India is the largest producer of cumin, accounting for about 70% of global production in the 2020–2021 fiscal year.
– Major cumin-producing countries include Syria, Turkey, UAE, and Iran.
– Cumin cultivation requires a long, hot summer of three to four months.
– The Mediterranean climate is most suitable for cumin’s growth.
– Cumin is grown from seeds and requires fertile, sandy, loamy soils with good drainage.
**Cumin Health Benefits**
– Cumin seeds have antibacterial properties due to their essential oil content.
– The essential oils and fatty acids in cumin seeds provide health benefits.
– Cumin seeds are rich in B vitamins, vitamin E, iron, magnesium, and manganese.
– Traditional medicinal uses of cumin include powdered forms for various ailments.
– No scientific evidence supports cumin seeds as a drug or medicine.
**Cumin in Culinary and Culture**
– Cumin seeds are widely used as a spice for flavor and aroma in various cuisines.
– Cumin has a significant cultural history, being used in ancient civilizations like Egypt, Greece, and India.
– Traditional cultivation practices of cumin involve sowing from October to early December in India.
– Cumin is essential in dishes like chili powder, curry blends, and traditional Indian mixtures.
– Cumin’s importance in ancient cultures and trade routes is notable.
**Cumin Plant and Growth**
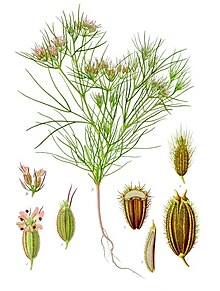
– Cumin is an annual herbaceous plant with specific growth requirements.
– Cultivation of cumin requires a long, hot summer of three to four months.
– Cumin plants are grown from seeds and prefer fertile, sandy, loamy soils with good drainage.
– Varieties of cumin plants are developed through breeding methods like sib mating and biotechnology.
– Cumin plants have 14 chromosomes and are bred to improve resistance to various stresses.
**Research and Analysis on Cumin**
– Studies have been conducted on salt tolerance and biochemical changes in cumin seeds.
– The United States Department of Agriculture has analyzed cumin seeds for various purposes.
– Research focuses on the essential oil analysis of cumin for its various applications.
– Methods for efficient regeneration of cumin plantlets have been developed.
– Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry is used for detailed analysis of cumin essential oil components.
Cumin (/ˈkʌmɪn/, /ˈkjuːmɪn/; US also /ˈkuːmɪn/; Cuminum cyminum) is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, native to the Irano-Turanian Region. Its seeds – each one contained within a fruit, which is dried – are used in the cuisines of many cultures in both whole and ground form. Although cumin is used in traditional medicine, there is no high-quality evidence that it is safe or effective as a therapeutic agent.
| Cumin | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae |
| Genus: | Cuminum |
| Species: | C. cyminum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cuminum cyminum | |
